Inhibiting the Protective Mechanism of Bacteria
Technion scientists have succeeded in inhibiting the protective mechanism of Salmonella bacteria by using substances originally developed to treat Alzheimer’s disease
They intend to continue this research direction toward developing innovative treatments that will neutralize virulent antibiotic-resistant bacteria

Associate Professor Meytal Landau (on the left) and Doctoral student Nir Salinas.
Researchers from the Technion Faculty of Biology were able to inhibit biofilm formation in Salmonella bacteria. Biofilm, a resistant layer of microorganisms that form on and coat various surfaces, constitutes a serious medical and environmental problem because it protects bacteria and enables them to attach to tissues, medical devices, pipes and more. The discovery made by Associate Professor Meytal Landau, doctoral student Nir Salinas, and the laboratory research team is expected to lead to the development of innovative treatments that will inhibit the antibiotic resistance of virulent bacteria.
In 2017, Prof. Landau’s research team published an article in Science describing new discoveries about Staphylococcus aureus—an especially virulent bacterium that has become resistant to many types of antibiotics and that is responsible for a considerable number of infections in hospitals and in the community. The researchers discovered that this bacterium, which attacks the organism’s T-cells of the immune systems, does so in part by means of secreting certain fibrils. These toxic fibrils resemble amyloids, proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, but differ from them structurally. In an article published in Nature Communication in 2018, Nir Salinas and his colleagues on the research team revealed their discovery that proteins from the same family as the toxic fibrils produce exceptionally stable amyloid structures that can survive under extremely difficult conditions and protect the bacteria. Prof. Landau expressed the hope that these discoveries will lead to new treatments that will impair the fibrils and significantly diminish the aggressively virulent infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
In a recent study in PLoS Pathogens, the Technion researchers suggested that by interfering with amyloid fibrils produced by E. coli and Salmonella, bacteria often linked with contaminated water or food, they can hamper the bacteria’s defense mechanisms and their ability to attach to tissues and medical devices. This is accomplished by repurposing substances that have already undergone clinical trials for treating Alzheimer’s. The major advantage of this repurposing is that the approval process is much shorter and less expensive than in the case of a new compound.
The substances tested on Salmonella bacteria do not harm the bacteria directly. Instead, they damage the biofilm, the resilient layer that protects bacteria from substances that pose a danger to them, including antibiotic drugs. The researchers estimate that this approach of impairing the biofilm will reduce the risk of developing resistance compared to antibiotics that kill the bacteria and thereby induce defense mechanisms against the drug, making the bacteria more resilient and virulent.
The research examined the possibility of damaging Salmonella and E. coli bacteria found in contaminated food. Nevertheless, the researchers hope their discovery will also be effective in battling other bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus. In his ongoing doctoral research, Mr. Salinas will focus on developing stable antibacterial substances and on examining small molecules that will interfere with the in-vitro assembly of amyloids in bacteria. He hopes these developments will accelerate the crucial battle against the development of virulent strains of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The research is being carried out in collaboration with the Institute for Complex Systems in Jülich and in Düsseldorf, Germany. The Technion Center for Structural Biology (TCSB), the Lorry Lokey Interdisciplinary Center for Life Sciences and Engineering, the Electron Microscopy Center, and the Center for Electron Microscopy of Soft Matter in the Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute (RBNI) also provided assistance for this project.
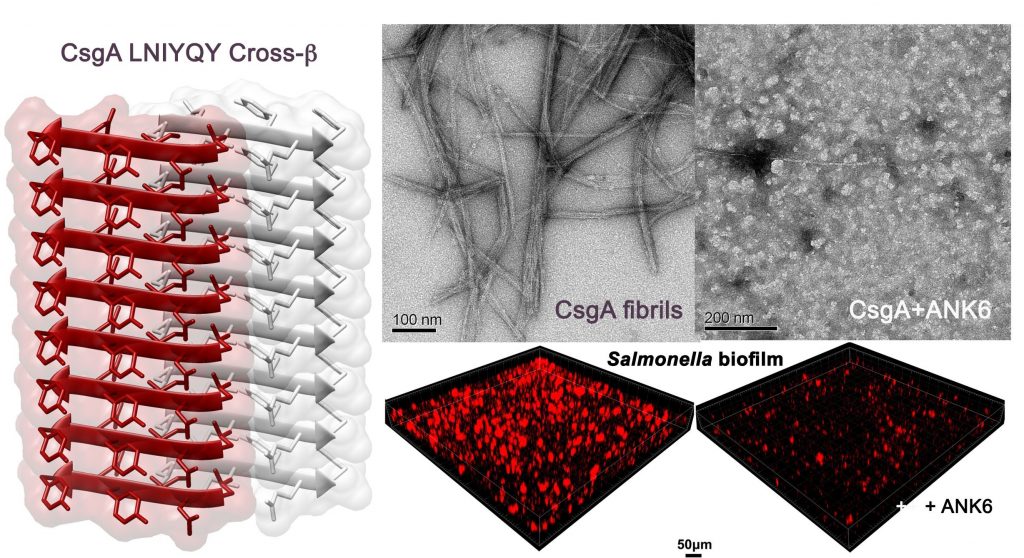
Image – Left: Atomic structure of a segment from a protein that forms fibrils that structure the biofilm of E. coli and Salmonella bacteria. This structure is highly similar to that of the amyloid fibrils related to Alzheimer’s disease, and this structural similarity inspired the idea of harming the bacterial biofilm fibrils using substances developed to combat Alzheimer’s fibrils.
Associate Professor Landau joined the Technion faculty after completing post-doctoral studies at UCLA, where she specialized in X-ray micro-crystallography of amyloids associated with Alzheimer’s disease. In September 2012 she founded her laboratory in the Faculty of Biology at the Technion.
Mr. Nir Salinas completed his bachelor’s degree in molecular biochemistry in the Schulich Faculty of Chemistry at the Technion. Today he is following a direct program to a doctoral degree in the Faculty of Biology.
For the article in PLoS Pathogens click here


